Mycorrhizal Relationships: Boosting Soil Fertility and Health

Understanding Mycorrhizal Relationships in Nature
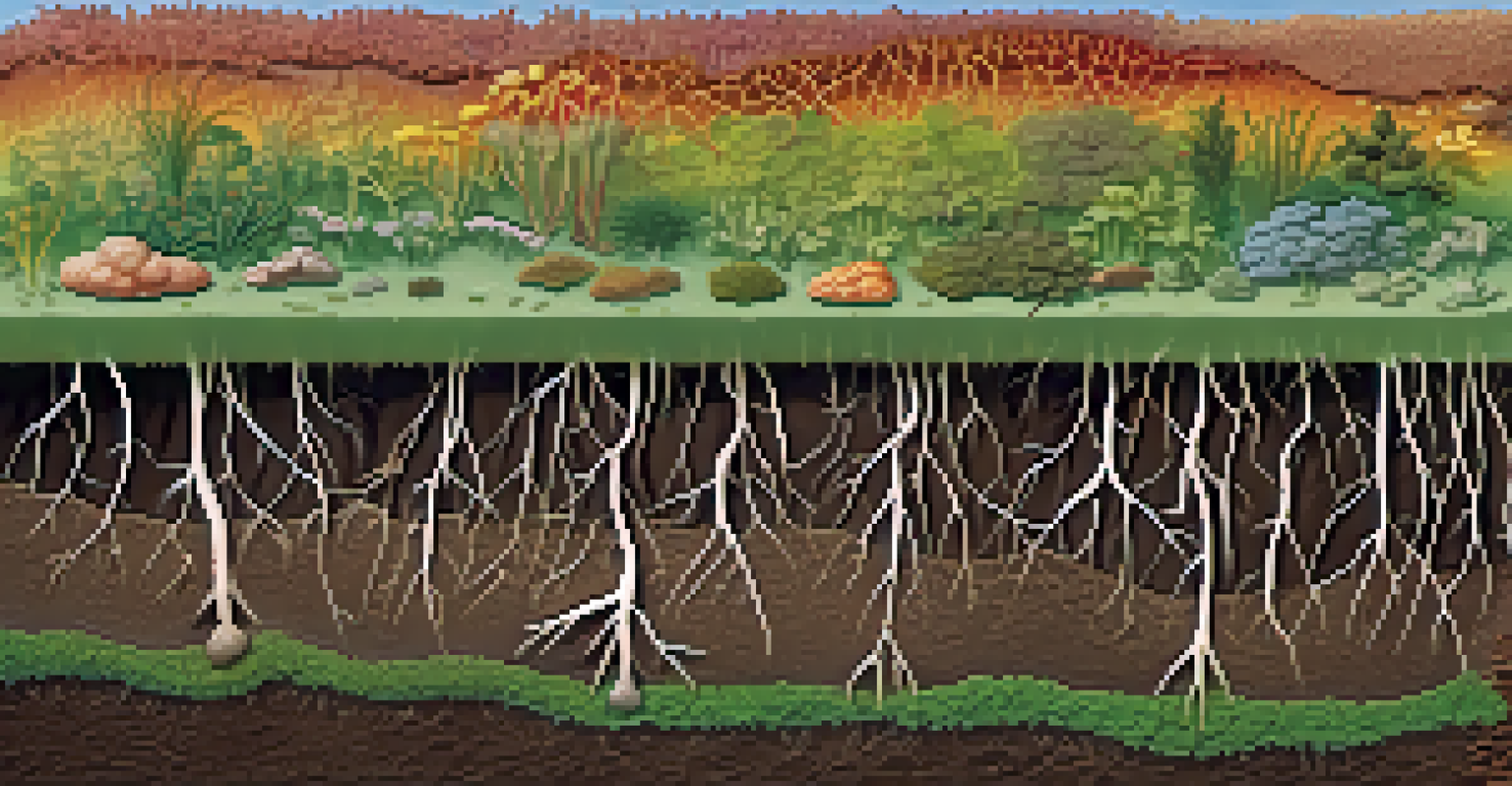
Mycorrhizal relationships are fascinating partnerships between fungi and plant roots. These interactions occur in about 90% of plant species, showcasing their crucial role in ecosystems. Essentially, the fungi extend their networks into the soil, accessing nutrients and water far beyond the plant's root zone.
The soil is alive, and its health is crucial for the health of the entire ecosystem.
In return, plants provide the fungi with carbohydrates produced during photosynthesis. This mutualistic relationship not only boosts the plant's growth but also enhances soil health. Think of it as a symbiotic dance where both partners thrive, leading to a more robust ecosystem.
Ultimately, understanding these relationships helps us appreciate the complexity of soil biology and the interconnectedness of life. As we delve deeper, we'll discover how these partnerships can significantly impact soil fertility.
How Mycorrhizae Enhance Nutrient Availability
One of the key benefits of mycorrhizal relationships is their ability to unlock nutrients for plants. The fungal hyphae act like tiny extensions of the plant roots, reaching into the soil to absorb essential minerals such as phosphorus, nitrogen, and potassium. This increased nutrient uptake can lead to healthier and more productive plants.

For example, plants with mycorrhizal associations can thrive in nutrient-poor soils where other plants might struggle. This ability to access nutrients makes mycorrhizae invaluable, especially in agricultural settings where soil fertility is often challenged. By fostering these relationships, farmers can enhance crop yields sustainably.
Mycorrhizae Boost Plant Growth
Mycorrhizal relationships enhance nutrient uptake, allowing plants to thrive even in nutrient-poor soils.
Furthermore, this enhanced nutrient availability can reduce the need for chemical fertilizers, promoting healthier ecosystems. As we transition to more sustainable agricultural practices, understanding and leveraging mycorrhizal relationships becomes increasingly essential.
The Role of Mycorrhizae in Soil Structure
Mycorrhizal fungi play a vital role in improving soil structure, which is crucial for healthy plant growth. As the fungal networks grow, they help bind soil particles together, creating a more stable and porous environment. This improved soil structure enhances aeration and water infiltration, both of which are essential for root health.
In nature, nothing exists alone.
Imagine a sponge soaking up water; mycorrhizae help create that sponge-like structure in the soil. This not only retains moisture but also allows roots to access it more efficiently. Healthy soil structure is like a well-organized city, where everything flows smoothly, benefiting the entire ecosystem.
Additionally, better soil structure helps prevent erosion and runoff, contributing to long-term soil health. By fostering mycorrhizal relationships, we can create more resilient landscapes that support diverse plant and animal life.
How Mycorrhizae Support Soil Microbial Communities
Mycorrhizal relationships also play a crucial role in supporting diverse microbial communities in the soil. The fungi create a habitat for beneficial microorganisms, which thrive in the environment fostered by mycorrhizae. These microbes contribute to nutrient cycling and organic matter decomposition, further enhancing soil fertility.
Think of mycorrhizae as the community center of the soil, where various microorganisms gather and collaborate. This vibrant microbial community helps break down organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the soil for plants to use. Without the support of mycorrhizae, many of these beneficial microbes might struggle to survive.
Improved Soil Structure
Mycorrhizal fungi improve soil structure, enhancing aeration and water retention, which is vital for plant health.
Moreover, a diverse microbial community helps protect plants from diseases by outcompeting harmful organisms. This balance of life in the soil is essential for sustainable agriculture and healthy ecosystems.
The Impact of Mycorrhizae on Climate Resilience
As we face climate change, mycorrhizal relationships can significantly enhance the resilience of ecosystems. By improving soil health and structure, these partnerships help plants better withstand extreme weather conditions, such as droughts and heavy rains. Healthy soils can retain more moisture and nutrients, making plants more adaptable.
For instance, during periods of drought, plants with mycorrhizal associations often survive better than those without. The fungi's extensive network allows for more efficient water uptake, giving these plants a fighting chance. This resilience is crucial as we navigate an increasingly unpredictable climate.
Furthermore, healthy soils contribute to carbon sequestration, helping mitigate climate change. By promoting mycorrhizal relationships, we are not only enhancing plant health but also taking steps toward a more sustainable future.
Practical Ways to Encourage Mycorrhizal Relationships
Encouraging mycorrhizal relationships in your garden or farm is easier than you might think. First and foremost, avoid using synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, as these can harm beneficial fungi and disrupt the delicate balance of soil life. Instead, opt for organic practices that support soil health.
Planting diverse species can also foster mycorrhizal relationships, as different plants can attract various fungi. Incorporating cover crops or companion planting can enhance this effect, promoting a rich underground network. Think of it as hosting a diverse potluck dinner, where each guest contributes something unique and valuable.
Support for Soil Microbes
These relationships create a habitat for beneficial microbes, promoting nutrient cycling and plant disease resistance.
Additionally, you can introduce mycorrhizal inoculants, which are commercially available products containing beneficial fungi. By adding these to your soil, you can jumpstart the establishment of mycorrhizal networks, helping your plants thrive.
The Future of Mycorrhizal Research and Agriculture
As our understanding of mycorrhizal relationships grows, so does the potential for innovative agricultural practices. Researchers are continually exploring how these partnerships can be harnessed to enhance food security and sustainability. This research paves the way for a more holistic approach to agriculture, prioritizing soil health.
For example, studies are underway to identify specific mycorrhizal fungi that can improve crop yields in various environments. By tailoring these relationships to specific crops and conditions, farmers could optimize their production while minimizing environmental impact. This personalized approach is akin to having a fitness coach who knows your unique needs.
The future of agriculture could very well hinge on understanding and incorporating mycorrhizal relationships into our farming practices. Embracing this knowledge can lead us toward a more sustainable and resilient agricultural system.