The Importance of Plant Structure in Ecosystem Functioning
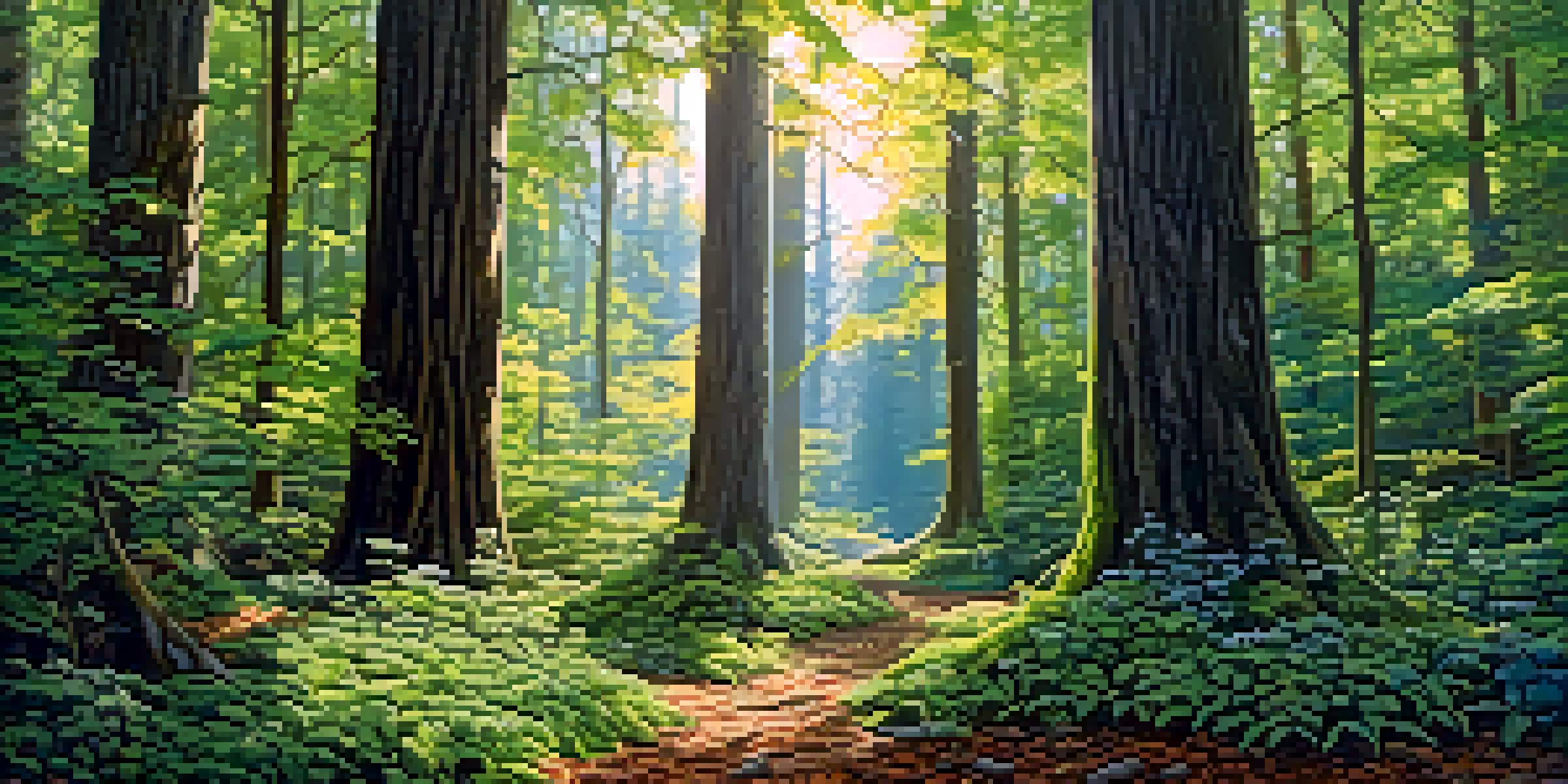

What is Plant Structure and Why Does it Matter?
Plant structure refers to the physical arrangement and organization of plants, including their roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. This structure plays a crucial role in how plants interact with their environment and contributes to overall ecosystem health. For instance, the height and density of plants can influence light availability, which affects photosynthesis and, consequently, energy flow within the ecosystem.
The clearest way into the Universe is through a forest wilderness.
When we think about forests, for example, the towering trees create a canopy that shelters smaller plants and animals below. This layered structure not only supports biodiversity but also helps regulate temperature and humidity within the ecosystem. Without such intricate plant structures, many species would struggle to survive, leading to a decline in ecological balance.
In essence, understanding plant structure helps us appreciate the complexities of nature. It’s not just about how a plant looks; it’s about how it functions within its habitat and the roles it plays in supporting life.
The Role of Roots in Ecosystem Stability
Roots are often the unsung heroes of plant structure, providing stability and anchoring plants to the soil. They play a vital role in preventing soil erosion, which can lead to loss of valuable topsoil and degradation of habitats. For example, in wetlands, the extensive root systems of grasses help to stabilize the soil, allowing for a diverse range of organisms to thrive in those environments.
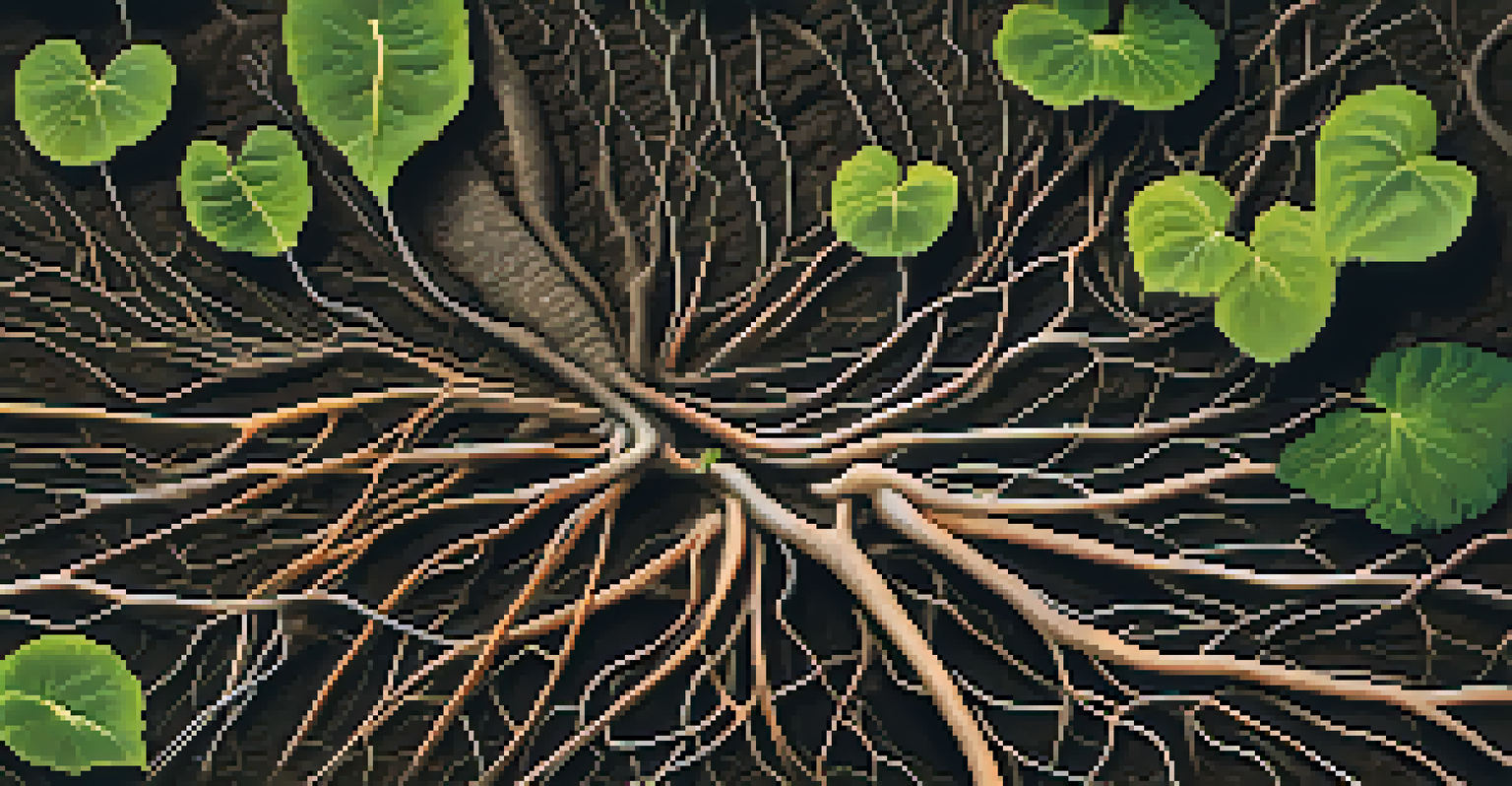
Moreover, roots are essential for nutrient uptake, absorbing water and minerals from the soil to support plant growth. This nutrient cycling is crucial not just for the plants themselves but for the entire food web, as herbivores depend on healthy plants for sustenance. The health of plant roots directly impacts the productivity of an ecosystem.
Plant Structures Support Ecosystems
Roots, stems, leaves, and flowers work together to maintain ecosystem health and biodiversity.
In summary, roots do much more than hold plants in place; they are a key component of ecosystem stability and health, demonstrating how interconnected these systems can be.
How Leaves Influence Photosynthesis and Energy Flow
Leaves are the primary sites for photosynthesis, the process that converts sunlight into energy for plants. The structure of leaves, including their size, shape, and arrangement, plays a significant role in maximizing light absorption. For instance, broad leaves can capture more sunlight, which can enhance the energy available for growth and reproduction.
In every walk with nature one receives far more than he seeks.
Additionally, the way leaves are structured affects transpiration, the process of water vapor loss from plants. This not only helps regulate plant temperature but also influences local humidity levels and climate. In turn, these changes can impact other organisms that rely on specific moisture levels in their habitats.
Thus, leaves are not just beautiful appendages; they are critical players in the energy dynamics of ecosystems, illustrating the intricate balance of life.
The Impact of Stems on Plant Communication and Support
Stems serve as the backbone of plants, providing structural support that allows them to grow tall and compete for sunlight. But there’s more to stems than just support; they also play an essential role in transporting nutrients and water between the roots and leaves. This transportation system is vital for maintaining the health of the entire plant, as it ensures that all parts receive the necessary resources.
Interestingly, stems also facilitate communication among plants. Some species can release chemicals through their stems to signal nearby plants about threats like herbivores. This can trigger defensive responses in neighboring plants, showcasing a remarkable level of cooperation within ecosystems.
Roots Prevent Soil Erosion
Roots anchor plants and help stabilize soil, which is vital for preventing erosion and supporting diverse habitats.
In conclusion, stems are multifunctional structures that not only support physical growth but also contribute to the interconnectedness of plant life, emphasizing the importance of plant structure in ecosystem functioning.
The Importance of Flowers in Reproductive Success
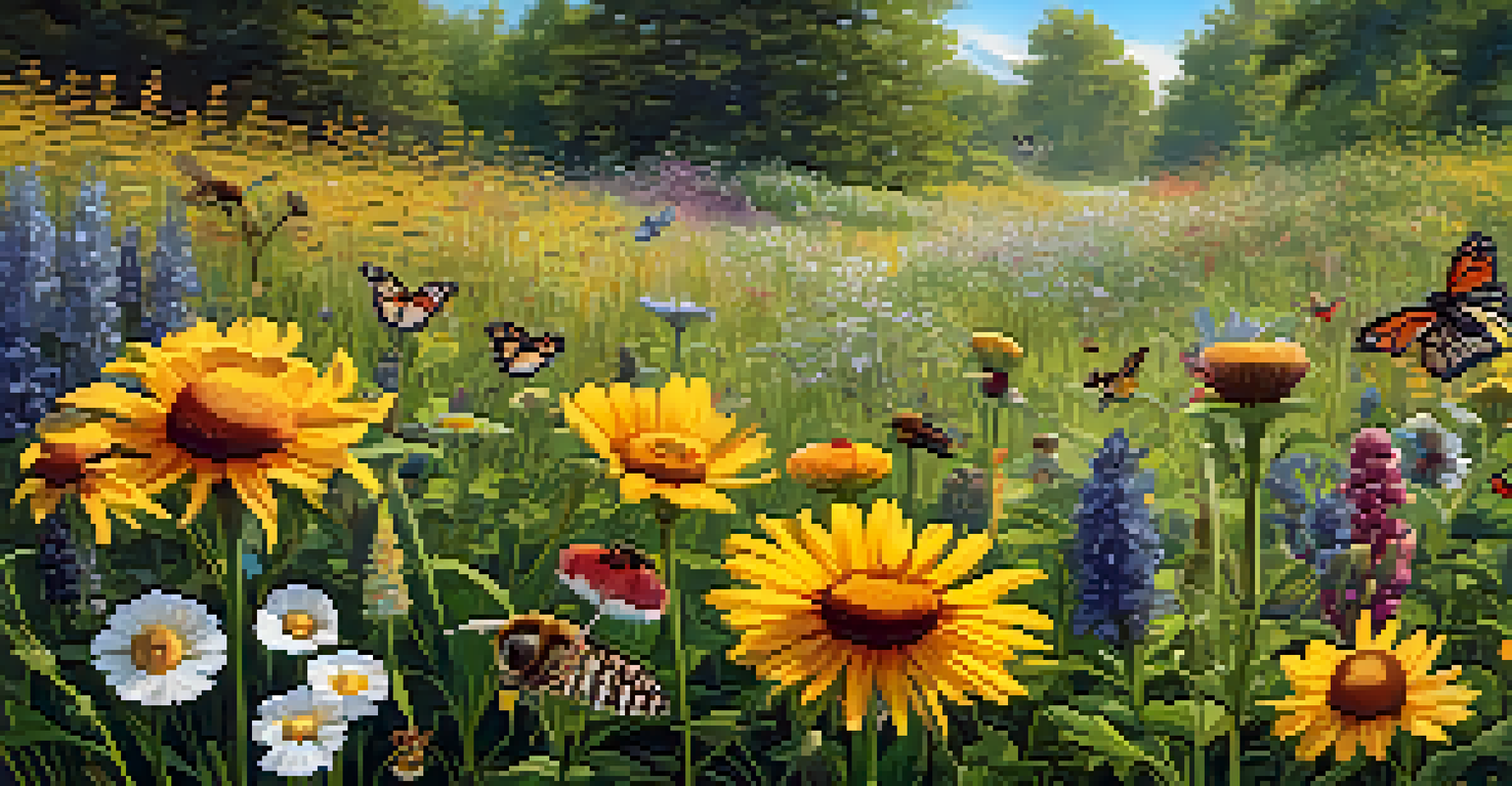
Flowers are often considered the most visually appealing part of a plant, but their importance extends far beyond aesthetics. They are crucial for reproduction, as they attract pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and birds. The structure of a flower, including its color, shape, and scent, plays a significant role in ensuring successful pollination and, subsequently, the production of seeds.
In addition to attracting pollinators, flowers also provide essential resources like nectar and pollen, which support a wide range of wildlife. This interaction not only helps plants reproduce but also supports the health of the entire ecosystem by sustaining pollinator populations. For instance, a decline in flowering plants can lead to a decrease in pollinator numbers, which can disrupt food chains.
Therefore, flowers are not only vital for the life cycle of plants but also serve as a bridge between various species in an ecosystem, highlighting the intricate web of life.
The Interdependence of Plant Structures and Ecosystem Health
The various structures of plants—roots, stems, leaves, and flowers—are interdependent and collectively contribute to ecosystem health. When one component is compromised, it can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem. For example, if root systems are damaged, it can lead to soil erosion and nutrient loss, ultimately affecting plant growth and the animals that depend on those plants.
Moreover, healthy plant structures also provide habitats for countless organisms, from insects to mammals. These organisms, in turn, contribute to pollination, seed dispersal, and nutrient cycling, illustrating the interconnectedness of life. A diverse array of plant structures supports a rich tapestry of life, promoting resilience in the face of environmental changes.
Human Impact Disrupts Plant Health
Deforestation and pollution negatively affect plant structures, leading to declines in ecosystem functionality and biodiversity.
In essence, the health of an ecosystem is closely tied to the integrity of plant structures. Protecting and preserving these structures is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem functionality.
Human Impact on Plant Structure and Ecosystem Functioning
Human activities, such as deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture, have significant impacts on plant structure and, consequently, ecosystem functioning. For instance, clearing forests for agriculture can disrupt the intricate relationships between plant structures and the animals that rely on them, leading to habitat loss and decreased biodiversity. This can initiate a domino effect, affecting not just plant life but entire food webs.
Furthermore, pollution can alter plant growth and health, affecting their ability to perform essential functions like photosynthesis and nutrient cycling. As plants struggle to survive in degraded environments, the overall health of the ecosystem declines, impacting everything from soil quality to water availability.

Recognizing the importance of plant structures in ecosystems is essential for conservation efforts. By understanding how our actions affect these structures, we can make more informed choices that promote sustainability and protect the intricate web of life.
Conclusion: Valuing Plant Structure for a Balanced Ecosystem
Understanding plant structure is crucial for appreciating its role in ecosystem functioning. Each component, from roots to flowers, plays a unique part in maintaining the balance of life. By valuing these structures, we can better understand the complexities of ecosystems and the interdependence of all living organisms.
As we face increasing environmental challenges, it becomes even more vital to protect and preserve plant structures. Healthy ecosystems are not only essential for wildlife but also for human well-being, providing resources like clean air, water, and food.
In conclusion, recognizing the importance of plant structure is a step toward fostering a sustainable future. By nurturing our natural ecosystems, we ensure a thriving planet for generations to come.