Understanding Plant Morphology: Key Concepts and Definitions

What is Plant Morphology and Why It Matters
Plant morphology is the study of the form and structure of plants. It encompasses everything from the shape of leaves to the arrangement of flowers. Understanding plant morphology is crucial for areas like botany, ecology, and agriculture, as it helps us learn how plants adapt to their environments.
Plants are the earth's endless source of beauty and wonder; they are nature's art in motion, adapting to their environment with grace and resilience.
For example, a plant's leaf shape can determine how efficiently it captures sunlight. In arid climates, you might find smaller or needle-like leaves that reduce water loss. By studying these adaptations, researchers can develop better strategies for crop cultivation in changing climates.
Moreover, plant morphology helps in identifying species and understanding their evolutionary relationships. By examining physical traits, scientists can infer how different plants have adapted over time, leading to a deeper appreciation of biodiversity.
Key Terms in Plant Morphology You Should Know
Several terms frequently pop up in discussions about plant morphology, and knowing them can enhance your understanding. 'Phytomorphology' refers to the study of the physical form of plants, while 'anatomy' focuses on the microscopic structures within plants. These distinctions are essential for researchers who delve into the complexities of plant life.
Another important term is 'phenotype,' which describes the observable characteristics of a plant, influenced by both genetics and environment. For instance, a sunflower's height or leaf color is part of its phenotype, showcasing how various factors can shape a plant's appearance.
Plant Morphology Affects Survival
The study of plant morphology reveals how physical traits, such as leaf shape and root structure, help plants adapt to their environments.
Additionally, 'morphogenesis' refers to the processes that cause plants to develop their shape and structure. This concept highlights how growth patterns can vary significantly depending on environmental cues, such as light and water availability, illustrating the dynamic nature of plant life.
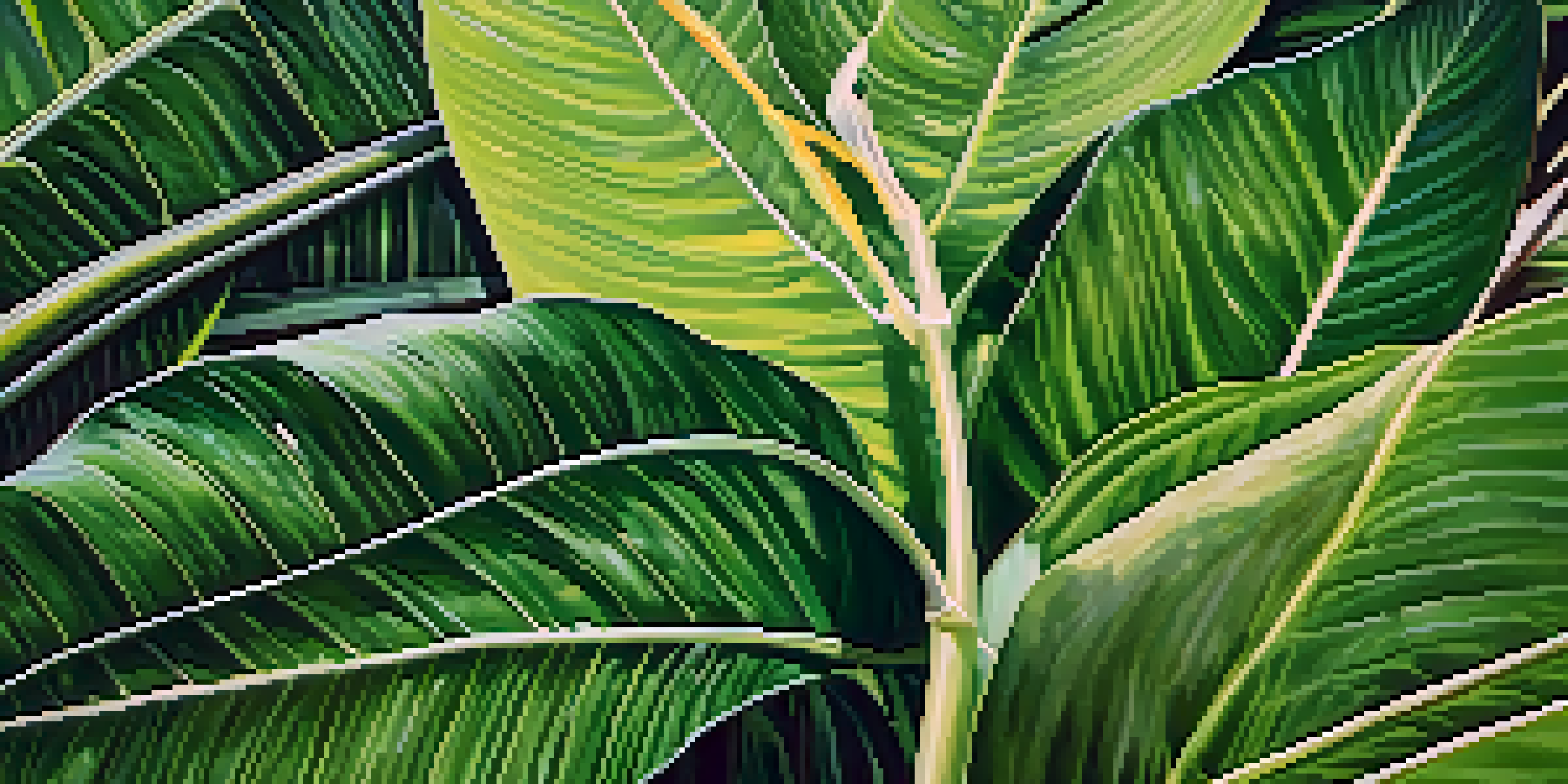
The Importance of Leaf Structure in Plants
Leaves play a critical role in a plant's ability to photosynthesize, which is how they convert sunlight into energy. The structure of a leaf, including its size, shape, and internal anatomy, directly impacts its efficiency. For example, broad leaves in tropical regions maximize sunlight capture, while smaller leaves in deserts minimize water loss.
Understanding the morphology of plants is not just about studying their structure, but about unlocking the secrets of their survival and the role they play in our ecosystems.
The arrangement of leaves on a stem, known as 'phyllotaxy,' is also significant. This arrangement allows for optimal light exposure while minimizing shade cast on lower leaves. In essence, the design of a leaf is a fine balance between maximizing energy intake and conserving resources.
Understanding leaf morphology can also help in assessing plant health and productivity. Farmers can use this knowledge to select appropriate crop varieties for their specific environments, leading to better yields and sustainable practices.
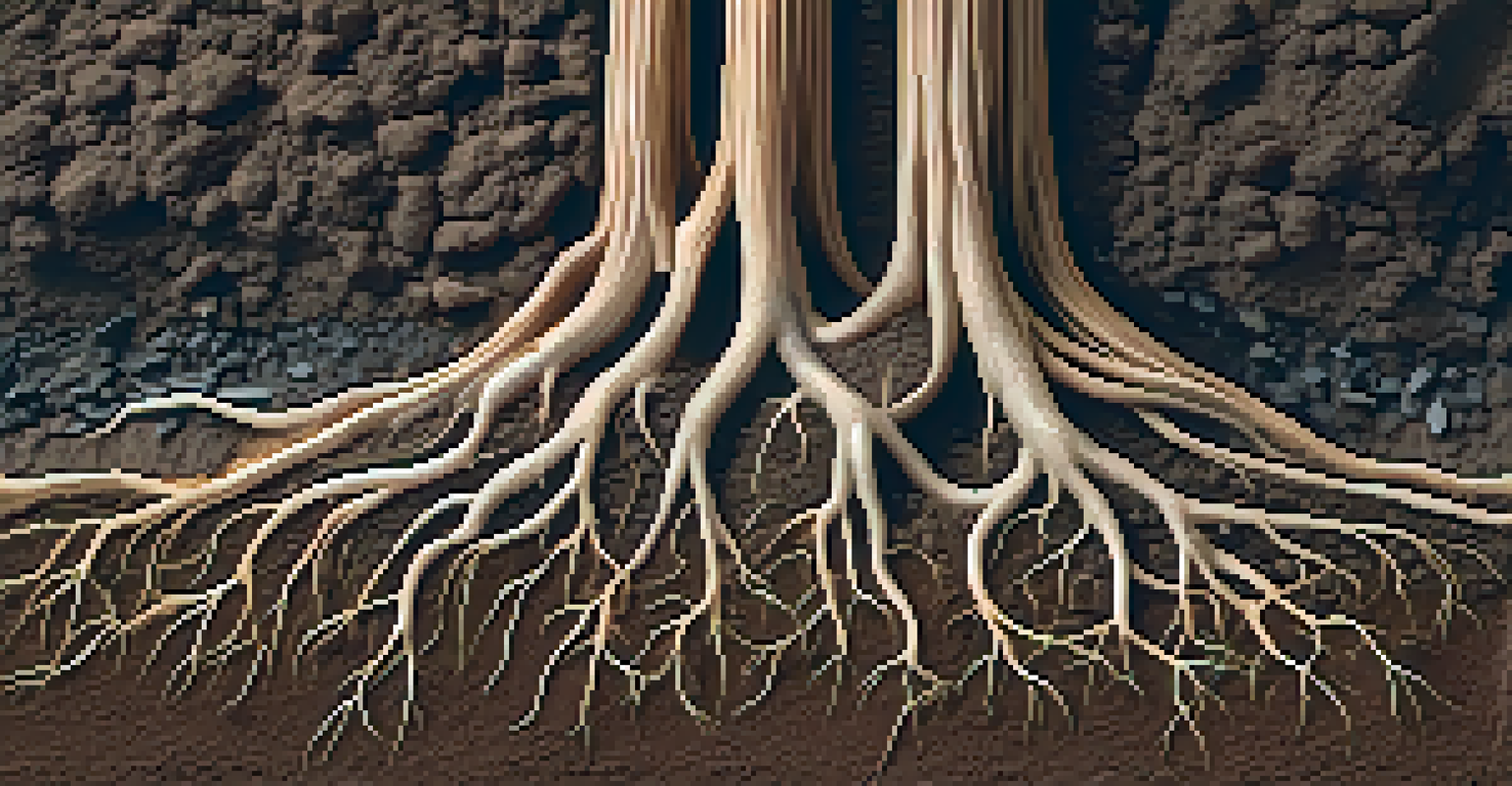
Roots: The Hidden Heroes of Morphology
While we often focus on visible parts of plants, roots are equally important for their stability and nutrient uptake. Root morphology varies widely among species, with some plants developing deep taproots for water access, while others might have shallow, fibrous roots that spread horizontally. This diversity helps plants adapt to their specific habitats.
For instance, desert plants often have extensive root systems that can absorb moisture from minimal rainfall. Conversely, aquatic plants may have specialized roots that allow them to anchor in soft substrates. Understanding these differences can provide insights into how plants thrive in various ecosystems.
Leaf Structure Impacts Photosynthesis
The size, shape, and arrangement of leaves are crucial for maximizing sunlight capture and minimizing water loss, directly influencing a plant's photosynthetic efficiency.
Moreover, root morphology influences soil health and structure. Healthy root systems can improve soil aeration and water retention, benefiting not just the plant but the larger ecosystem. Thus, studying root morphology is essential for sustainable land management and agriculture.
Understanding Stems: Support and Transport Systems
Stems serve as the backbone of a plant, providing support and facilitating the transport of nutrients and water between roots and leaves. The morphology of stems varies significantly, from the thick trunks of trees to the slender stems of herbs. Each design serves a purpose, aiding the plant in its environment.
For example, climbing plants often have flexible stems that allow them to reach for sunlight by wrapping around structures. These adaptations are crucial for survival in dense forests where light is limited. In contrast, desert plants may have thick, fleshy stems to store water, demonstrating how morphology is tied to ecological needs.
Additionally, the internal structure of stems, including vascular tissues, plays a vital role in their function. Understanding stem morphology helps researchers and horticulturists develop better plant management strategies, as it directly affects growth and overall health.
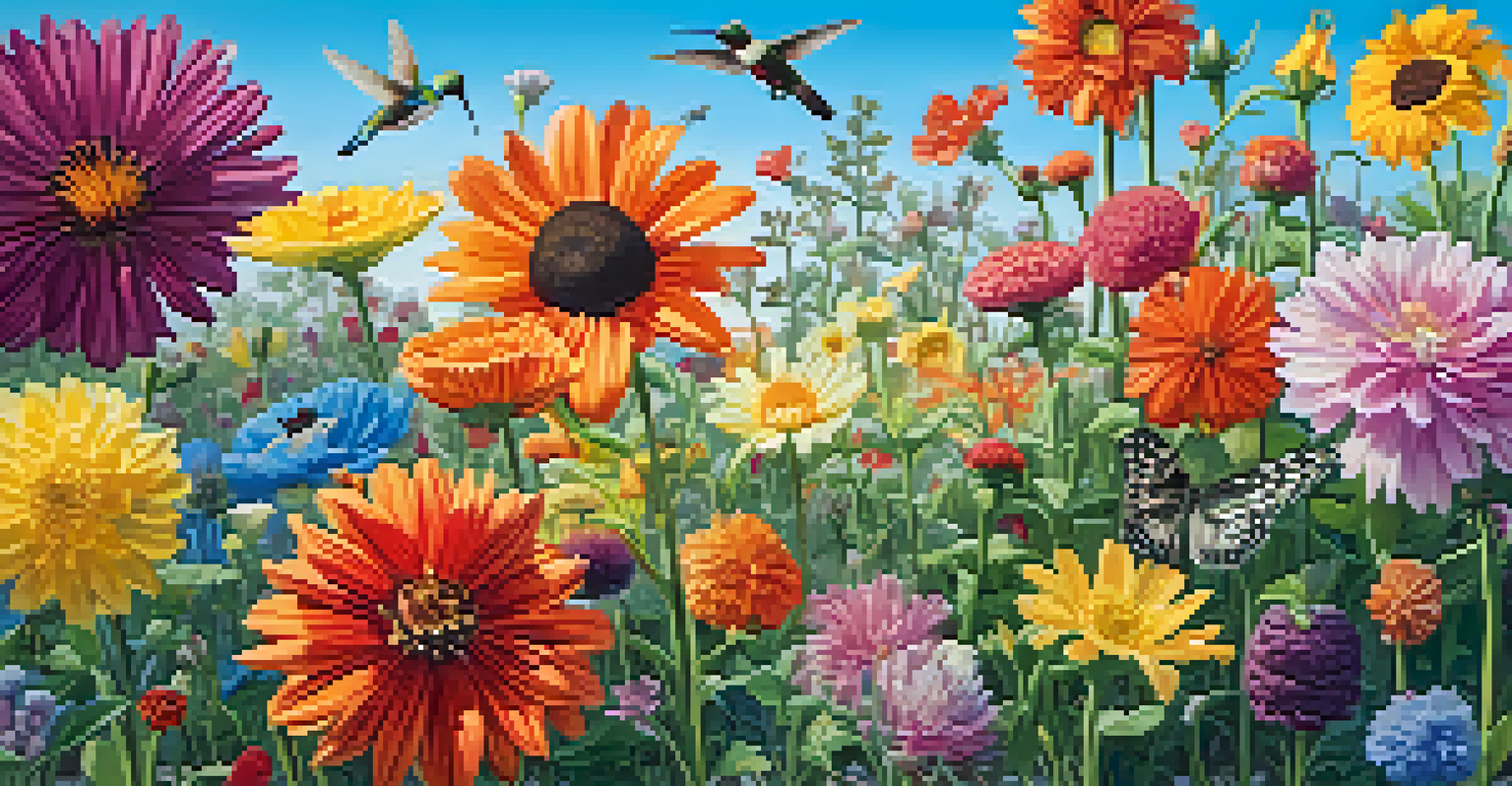
Flowers and Reproduction: The Morphological Marvels
Flowers are not just beautiful; they are critical for reproduction in many plants. Flower morphology can vary greatly, with different shapes, sizes, and colors attracting specific pollinators. This diversity is an evolutionary strategy that ensures successful reproduction.
For instance, tubular flowers are often designed to attract hummingbirds, while flat, open flowers may appeal to bees. By studying flower morphology, scientists can understand how plants interact with their environment and adapt to attract the right pollinators for reproduction.
Roots Support Ecosystem Health
Root morphology plays a vital role in nutrient uptake and soil health, highlighting its importance in sustainable agriculture and land management.
Moreover, the arrangement of floral parts—like petals, sepals, and stamens—can influence pollination success. Understanding these structures can provide insights into plant breeding and conservation efforts, highlighting the importance of flower morphology in maintaining biodiversity.
The Role of Morphology in Plant Adaptations
Morphological adaptations are key to a plant's survival in varying environments. These adaptations can be physical, like thicker leaves in arid conditions, or structural, such as the development of deep roots in sandy soils. Each adaptation allows plants to thrive where they are planted.
For example, in cold climates, some plants develop antifreeze proteins that prevent ice from forming within their tissues. Meanwhile, others might have tough, waxy coatings on their leaves to reduce water loss in hot, dry areas. These adaptations illustrate the incredible resilience of plants and their ability to evolve.

Understanding these adaptations through morphology not only enhances our knowledge of plant biology but also informs conservation strategies. By recognizing how plants adapt, we can better protect vulnerable species and their habitats.