Understanding Plant Taxonomy: A Guide to Classification Basics
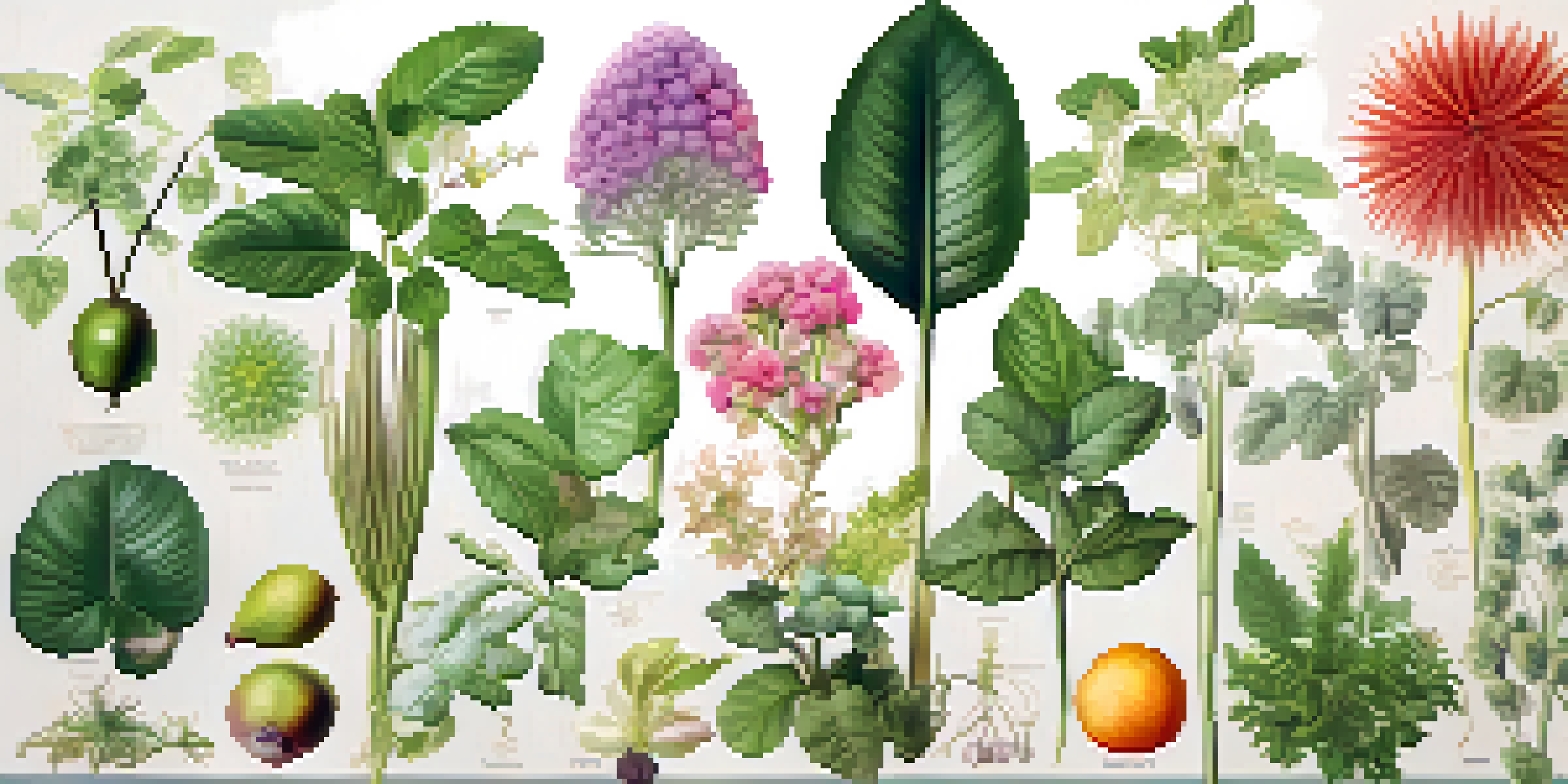

What is Plant Taxonomy and Why Does It Matter?
Plant taxonomy is the science of classifying plants based on shared characteristics. Think of it as a way to organize the plant kingdom into a neat filing system, making it easier to study and understand the vast diversity of plant life. This classification not only helps botanists communicate effectively but also plays a crucial role in conservation efforts.
The plant kingdom is a vast and varied tapestry, and taxonomy is the thread that weaves it all together.
By categorizing plants, we can identify species, understand their relationships, and track their evolutionary history. For example, knowing that roses and strawberries share a common ancestor helps us appreciate their similarities and differences. Without taxonomy, the world of plants would be an overwhelming jumble of names and forms, making research and conservation much more challenging.
In essence, plant taxonomy simplifies the complex web of life, enabling scientists, horticulturists, and even casual gardeners to navigate through the multitude of plant species with ease and confidence.
The Hierarchical Structure of Taxonomy Explained
Plant taxonomy is organized in a hierarchical structure, often depicted as a tree with various branches. At the top, you have the broadest category, the kingdom, which for plants is the Plantae kingdom. As you move down the tree, the categories become more specific, leading to divisions such as phylum, class, order, family, genus, and finally, species.

Each level of this hierarchy helps refine our understanding of plants. For instance, within the family Rosaceae, you’ll find different genera like Rosa (roses) and Fragaria (strawberries). This structured approach not only provides clarity but also highlights the evolutionary relationships between different plants, illustrating how they are interconnected.
Understanding Plant Taxonomy
Plant taxonomy classifies plants to simplify the study of their diversity and relationships.
By using this hierarchical system, botanists can better categorize new discoveries and understand where they fit within the larger context of plant life. It’s like having a detailed roadmap that guides researchers through the intricate landscape of plant diversity.
The Importance of Binomial Nomenclature
Binomial nomenclature is a formal system of naming species using two Latin words: the genus name and the species identifier. This system, developed by Carl Linnaeus in the 18th century, provides a universal language for botanists around the globe. For example, the scientific name for the common sunflower is Helianthus annuus, which helps avoid confusion caused by local common names.
Taxonomy is not just a classification; it's a roadmap that helps us navigate the vast diversity of life on Earth.
Using this naming convention is essential, especially since many plants have multiple common names depending on the region. Imagine trying to find information on a 'bluebell'—it could refer to several different plants! By employing binomial nomenclature, we ensure that everyone is on the same page, reducing ambiguity in scientific communication.
Moreover, this system also reflects the hierarchical structure of taxonomy, as the genus indicates a broader category under which related species are grouped. It's a simple yet effective method to categorize the stunning variety of plant life in our world.
How Plant Families Are Determined
Plant families are groups of related plants that share common characteristics and evolutionary traits. Determining these families involves studying various features, including flower structure, leaf arrangement, and fruit types. For example, plants in the same family often exhibit similar reproductive structures, which can be a key indicator of their familial ties.
This classification isn't just about looks; it also involves genetic analysis to uncover deeper connections. With advancements in molecular biology, botanists can use DNA sequencing to confirm relationships between plants that may look quite different on the surface. This blend of traditional morphology and modern science enriches our understanding of plant families.
Importance of Binomial Nomenclature
Binomial nomenclature provides a universal naming system that reduces confusion among plant species.
Understanding plant families is crucial for conservation efforts, agriculture, and horticulture. By recognizing which plants are related, we can better predict how they might respond to environmental changes or diseases, ultimately helping to protect our plant biodiversity.
Recognizing Plant Genera and Their Significance
A genus is a group of species that are closely related and share a common ancestor. For example, the genus Quercus includes all oak trees, showcasing the diversity within a single group. Recognizing genera helps botanists categorize and study plants more effectively, as members of the same genus often exhibit similar characteristics.
The delineation of genera is based on various traits, including flower structure, leaf form, and growth habits. This helps researchers make educated guesses about the ecological roles and potential uses of related plants. For instance, knowing that oaks and beeches are in the same genus can provide insights into their similar habitats and growth patterns.
Understanding genera is also essential for gardening and landscaping, as it allows enthusiasts to select plants that are not only beautiful but also compatible with each other. It's like finding dance partners at a party; knowing who fits well together can lead to a more harmonious garden.
Species Classification: The Final Frontier
At the end of the taxonomy ladder lies the species, the most specific classification. A species is defined as a group of plants that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. For example, within the genus Rosa, the species Rosa rubiginosa is known as sweet briar rose, which has distinct characteristics that set it apart from other roses.
Identifying a species requires careful observation of physical traits and reproductive habits. This can sometimes be challenging, as some plants exhibit significant variation within a species due to environmental factors. However, understanding these nuances is vital for conservation efforts, as protecting a species often means preserving its genetic diversity.
Technology Enhances Plant Classification
Advancements in technology, like DNA sequencing, make plant taxonomy more accurate and efficient.
Moreover, recognizing a species helps in the effective management of ecosystems. By understanding which species thrive under certain conditions, we can better support biodiversity and promote healthy environments for various plant and animal life.
The Role of Technology in Modern Taxonomy
Technology has transformed the field of plant taxonomy, making classification more efficient and accurate than ever before. Tools like DNA sequencing and bioinformatics allow researchers to analyze genetic material, providing deeper insights into the relationships between different species. This data-driven approach helps clarify classifications that were once based solely on physical characteristics.
Additionally, digital databases and online resources have made it easier for botanists to share information and collaborate across the globe. Websites and apps that provide access to taxonomic information enable both professionals and enthusiasts to explore plant relationships and characteristics with just a few clicks. Imagine having an entire library of plant knowledge right in your pocket!
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more developments in plant taxonomy. This will not only enhance our understanding of plant diversity but also support conservation efforts and sustainable practices in agriculture and horticulture.