Soil pH and Its Impact on Plant Growth and Fertility

What is Soil pH and Why It Matters for Plants
Soil pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the soil, ranging from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral, while values below 7 indicate acidity and those above indicate alkalinity. Understanding soil pH is crucial because it influences nutrient availability and microbial activity, both of which are vital for plant health.
Soil is a living system, and its health is fundamental to the health of plants, animals, and humans alike.
For instance, most plants thrive in slightly acidic to neutral soil, usually between pH 6 and 7. If the pH is too low or too high, certain nutrients can become locked away, making them unavailable to plants. This can lead to deficiencies that stunt growth or impair overall health.
By knowing your soil's pH, you can make informed decisions about amendments and fertilizers to optimize your garden. Testing your soil pH is straightforward and can be done with kits available at garden centers or through local extension services.
How Soil pH Affects Nutrient Availability
Soil pH significantly impacts how well plants can absorb nutrients. For example, iron is only available to plants in acidic soils, while elements like calcium thrive in alkaline conditions. When soil pH strays too far from the ideal range, it can create a nutrient imbalance, leading to deficiencies.
A classic example is the nutrient nitrogen, which is essential for plant growth. In highly acidic soils, nitrogen can leach away, resulting in poor growth. On the other hand, alkaline soils may cause certain nutrients like manganese to become less available, impacting overall plant vitality.
Soil pH Affects Plant Health
Soil pH influences nutrient availability and microbial activity, which are critical for plant growth.
This relationship between pH and nutrient availability highlights the importance of regularly monitoring soil pH. By maintaining it within the optimal range, gardeners can ensure that plants have access to the nutrients they need for robust growth.
The Role of Soil Microbes and pH Levels
Soil microbes play a crucial role in breaking down organic matter and making nutrients available to plants. However, these beneficial microorganisms have their preferences too, including optimal pH levels. Most soil microbes prefer a slightly acidic to neutral environment, which allows them to thrive.
The soil is the great connector of our lives, the source and destination of all.
When soil pH is too low or too high, microbial activity can decrease, limiting the decomposition of organic materials. This can slow down nutrient cycling, ultimately affecting plant growth. For instance, if beneficial bacteria that convert nitrogen from the atmosphere into a form plants can use are less active, it can stunt plant development.
Thus, maintaining a balanced soil pH not only benefits plants directly but also supports the microbial communities that enhance soil fertility. By fostering a healthy microbial ecosystem, gardeners can improve their soil's overall health and productivity.
Testing and Adjusting Soil pH for Optimal Growth
Testing your soil's pH is the first step in understanding its health. Home testing kits are easy to use and provide immediate results, while local agricultural extensions can offer more precise analyses. Knowing your soil pH allows you to make necessary adjustments to ensure optimal growing conditions.
If your soil is too acidic, adding lime can help raise the pH, while sulfur can lower the pH in alkaline soils. It's essential to make these adjustments gradually, as sudden changes can shock your plants. Regular testing after amendments is also crucial to monitor progress and ensure you stay within the desired range.
Testing pH for Garden Success
Regularly testing and adjusting soil pH ensures optimal growing conditions for various plants.
By actively managing soil pH, you empower your plants to reach their full potential. This proactive approach not only enhances growth but also leads to healthier and more fruitful plants.
Plants and Their Preferred Soil pH Ranges
Different plants have varying preferences when it comes to soil pH. For example, blueberries thrive in acidic soils with a pH of 4.5 to 5.5, while asparagus prefers a more alkaline environment, ideally around 7.0 to 8.0. Understanding these preferences is key to successful gardening or farming.
If you are growing a diverse garden, consider grouping plants with similar pH requirements. This way, you can create an environment that meets the needs of all plants involved. Mixing plants with different pH needs can lead to competition and stress, ultimately reducing yields.
By researching the specific pH preferences of your plants, you can tailor your soil management practices accordingly. This knowledge empowers you to create an optimal growing environment that promotes healthy plants and bountiful harvests.
The Impact of Soil pH on Crop Yields
Soil pH plays a significant role in determining crop yields. When pH levels are optimal, plants can access the nutrients they need, leading to healthy growth and bountiful harvests. Conversely, poor pH management can result in stunted growth and lower yields, which can have economic implications for farmers.
For instance, a farmer who neglects soil pH might experience diminished yields, prompting them to use more fertilizers to compensate for nutrient deficiencies. This not only increases costs but can also lead to environmental issues, such as runoff that pollutes waterways.
Misconceptions About Soil pH
Many gardeners incorrectly believe that all plants can thrive in any pH level, ignoring specific needs.
By prioritizing soil pH management, you invest in the long-term health of your crops and the sustainability of your farming practices. It's a win-win for both productivity and environmental stewardship.
Common Misconceptions About Soil pH
Many people mistakenly believe that all plants can thrive in any soil pH. In reality, each plant species has unique pH preferences that can significantly affect their growth. Ignoring these preferences can lead to disappointing gardening results, despite best efforts.
Another common misconception is that soil pH cannot be changed. While it does require time and effort, adjustments can be made through the application of specific soil amendments. Understanding that soil pH is dynamic and can be managed empowers gardeners to take control of their growing conditions.
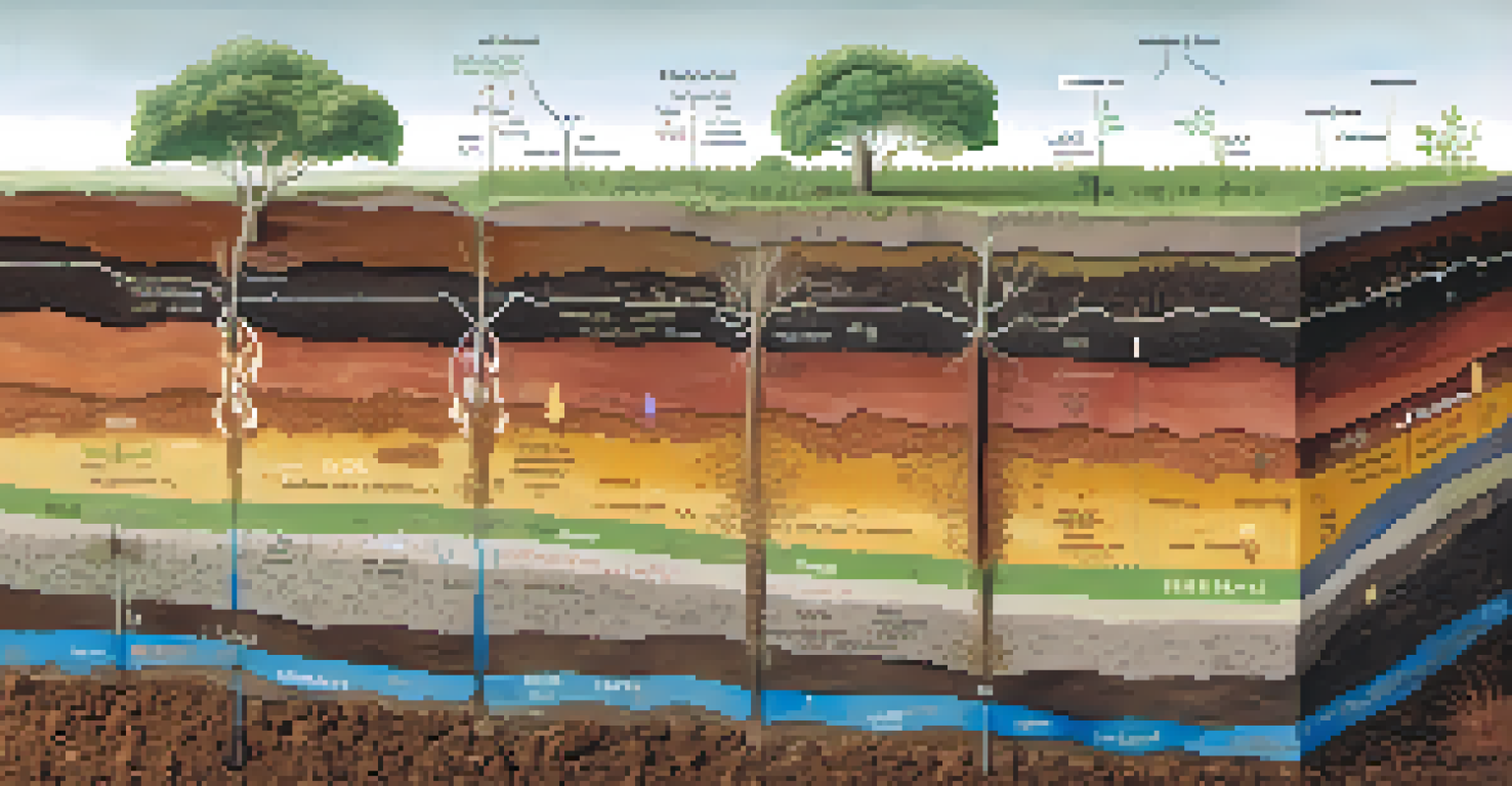
By debunking these misconceptions, gardeners can make more informed decisions that lead to healthier plants and better yields. Knowledge about soil pH is an essential tool in any gardener's toolkit.