The Connection Between Soil Health and Plant Microbiomes

Understanding Soil Health and Its Importance
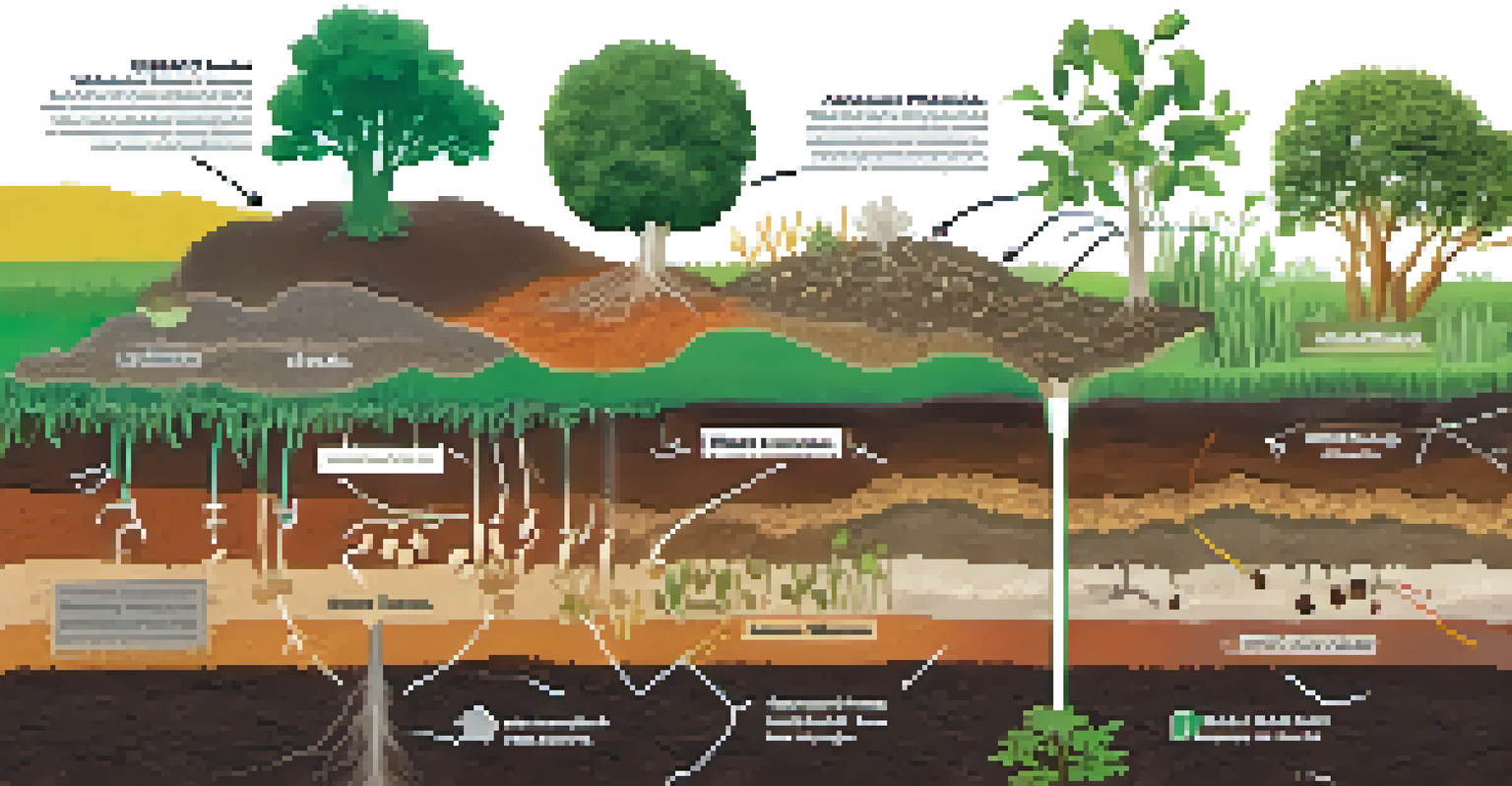
Soil health is a term that refers to the condition of soil and its ability to support plant life. Healthy soil is rich in nutrients, has good structure, and supports diverse organisms. This fundamental aspect of agriculture affects not only the growth of plants but also the broader ecosystem in which they exist.
Healthy soil is the foundation of healthy food, healthy people, and a healthy planet.
When soil is rich in organic matter and has a balanced pH, it creates an ideal environment for various microorganisms. These microorganisms play a crucial role in nutrient cycling, breaking down organic matter into forms that plants can readily absorb. Thus, the health of the soil directly influences the availability of nutrients to plants.
In essence, healthy soil is like a well-oiled machine, where every component works together to create a thriving environment for plants. Neglecting soil health can lead to problems such as nutrient deficiencies, which can stunt plant growth and reduce yields.
What Are Plant Microbiomes?
Plant microbiomes consist of a diverse community of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and archaea, that live in and around plant roots. These tiny organisms form relationships with plants, helping them absorb nutrients and water more efficiently. You can think of plant microbiomes as a supportive network that enhances a plant's health.

These microbiomes can vary significantly between different plant species and even among individual plants of the same species. Factors such as soil type, climate, and management practices can influence the composition and diversity of these microbial communities. This variability emphasizes the intricate relationship between plants and their microbial companions.
Soil Health Supports Plant Growth
Healthy soil provides essential nutrients and a thriving environment for plants, directly influencing their growth and resilience.
Understanding plant microbiomes is essential, as they are pivotal in plant development, disease resistance, and stress tolerance. A healthy microbiome can act as a protective barrier against pathogens, much like how a good immune system protects our bodies.
The Role of Soil in Shaping Plant Microbiomes
Soil acts as a habitat for the microorganisms that form plant microbiomes, providing them with the nutrients and conditions they need to thrive. The physical and chemical properties of the soil, such as texture and moisture content, directly impact which microorganisms can flourish in a given environment. This means that changes in soil health can lead to shifts in the microbiome composition.
The soil is the great connector of our lives, the source and destination of all.
For instance, compacted soil with low organic matter may harbor fewer beneficial microbes, which could impede plant growth and health. On the other hand, well-aerated and nutrient-rich soil encourages a diverse and thriving microbiome. This relationship highlights the importance of maintaining soil health to support robust plant microbiomes.
Additionally, the interactions between soil microorganisms and plants can lead to synergistic effects that benefit both parties. Healthy soil not only nurtures the microbiome but also allows plants to express their full potential by enhancing their growth and resilience.
How Practices Affect Soil Health and Microbiomes
Agricultural practices play a significant role in determining both soil health and the composition of plant microbiomes. For example, intensive farming often relies on chemical fertilizers and pesticides, which can disrupt the natural balance of soil life. This disruption can hinder the development of beneficial microbial communities that plants rely on for optimal health.
Conversely, sustainable practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and organic amendments can improve soil health and encourage diverse microbial populations. These practices help to build soil organic matter, enhance nutrient availability, and improve soil structure, creating an environment where beneficial microbes can flourish.
Microbiomes Enhance Plant Health
Plant microbiomes, consisting of beneficial microorganisms, form supportive relationships with plants, improving nutrient absorption and disease resistance.
By adopting practices that prioritize soil health, farmers can enhance the resilience of their crops, which translates to better yields and reduced reliance on chemical inputs. This creates a win-win situation for both the farmer and the environment.
The Benefits of Healthy Soil and Microbiomes
Healthy soil and robust plant microbiomes are intertwined, offering numerous benefits to both plants and the environment. One of the primary advantages is improved nutrient cycling, which leads to enhanced plant growth and productivity. When soil is healthy, it can provide plants with the essential nutrients they need to thrive, resulting in bountiful harvests.
Additionally, a thriving microbiome enhances plants' resilience to diseases and environmental stresses such as drought or flooding. For example, certain beneficial fungi can help plants absorb more water, which is especially important during dry spells. This natural support system can help reduce the need for chemical interventions, fostering a more sustainable approach to agriculture.
Moreover, healthy soil contributes to overall ecosystem health by supporting biodiversity, improving water retention, and reducing erosion. This interconnectedness highlights how maintaining soil health is essential not just for agricultural productivity but also for preserving our planet's ecological balance.
Future Directions in Soil and Microbiome Research
The relationship between soil health and plant microbiomes is a growing area of interest for researchers and farmers alike. As we gain a deeper understanding of these connections, innovative strategies can be developed to improve soil management practices. This research is critical for addressing global challenges such as food security and climate change.
Emerging technologies, such as metagenomics, allow scientists to study the genetic material of microbial communities in soil. This can lead to insights into how specific microbes contribute to plant health and soil function. With this knowledge, farmers can adopt tailored approaches that promote beneficial microbes while suppressing harmful ones.
Sustainable Practices Boost Soil Vitality
Implementing sustainable agricultural practices can enhance soil health and microbiome diversity, leading to better crop yields and environmental benefits.
Looking ahead, the integration of soil health and microbiome management into agricultural practices will likely become more common. This holistic approach can help create resilient farming systems that are capable of thriving in the face of environmental challenges.
Conclusion: Nurturing Soil for Healthier Plants
In conclusion, the connection between soil health and plant microbiomes is undeniable. Healthy soil fosters a diverse and thriving microbiome that plays a critical role in supporting plant growth and resilience. By prioritizing soil health through sustainable practices, we can enhance both agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability.
As we continue to explore this dynamic relationship, it's clear that nurturing our soil is essential for the health of our plants and the future of our food systems. Adopting practices that promote soil health not only benefits individual farmers but also contributes to the well-being of our planet.
Ultimately, the journey towards healthier soil and plants requires a collective effort from farmers, researchers, and consumers alike. Together, we can cultivate a future where soil health and plant microbiomes thrive in harmony.